-
The Executive Health Assessment
Who: anyone interested in their health status
1. Blood Pressure
2. ECG (Heart rate & rhythm)
3. Lung Exhalation & Inhalation
..............................................................
4. HbA1c Blood Glucose %
5. Triglycerides
6. Uric Acid
..............................................................
7. Comprehensive Body Scan (Muscle, Fat, Bone, Water)
..............................................................
8. Grip Strength
-
#
Test
Potentially Risky
AUS Averages
Good
Excellent
1
Blood Pressure (mm/Hg)
<150/<100
135/85
120/80
110/75
2a
ECG – Resting Heart Rate (BPM)
F:95>, M:95>
F:85M:80
F:75, M:70
F:<65, M:<60
2b
ECG – Normal Rhythm
AF
Normal
Normal
Normal
3a
Lung Maximal Power (Litr) - Exhalation
F:<1.0, M:<2.0
F:2.1, M:2.8
F:2.8, M:3.5
F:3.5>, M:5>
3b
Lung Maximal Power (secs) - Inhalation
F:1, M:1
F:3, M:2
F:4, M:4
F:6, M:6
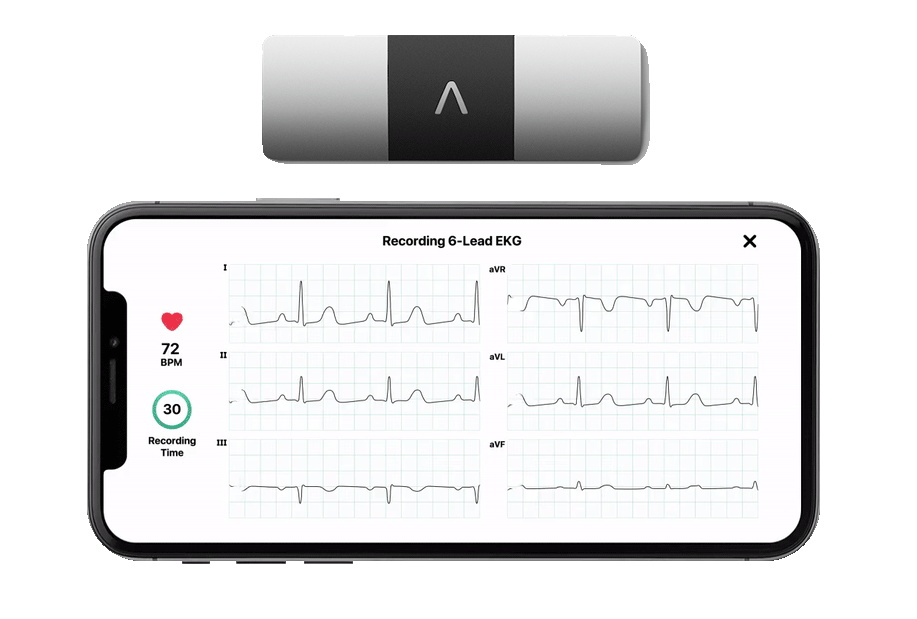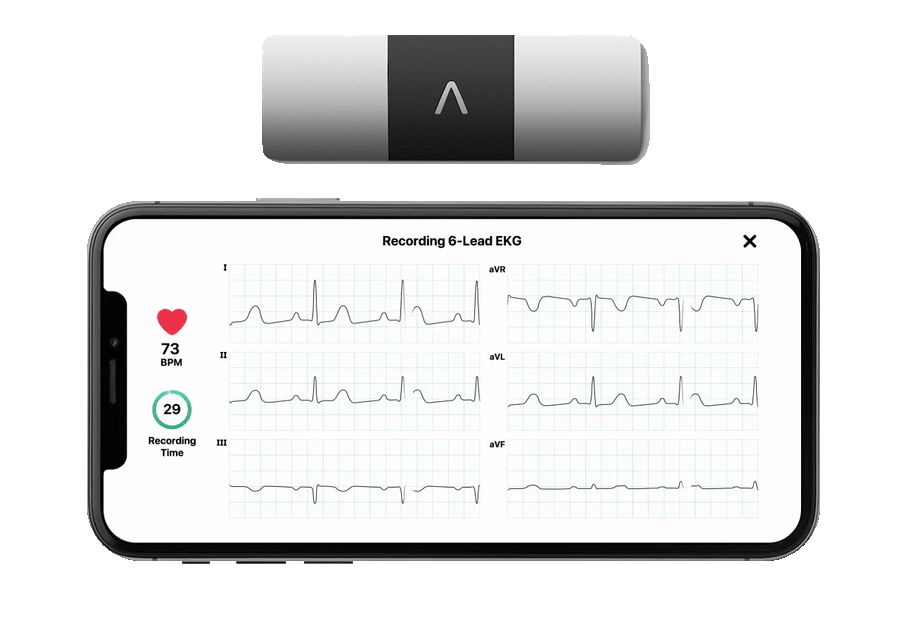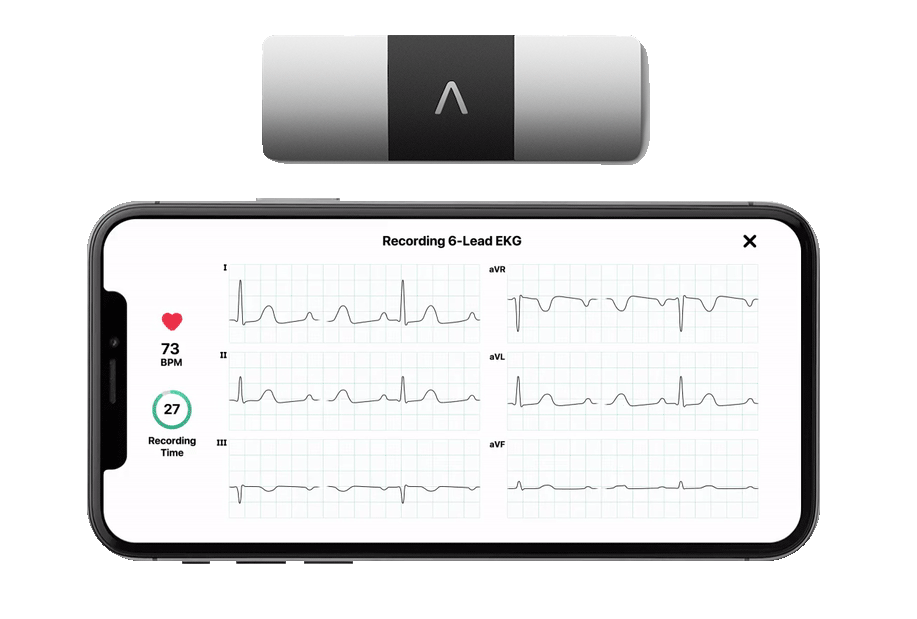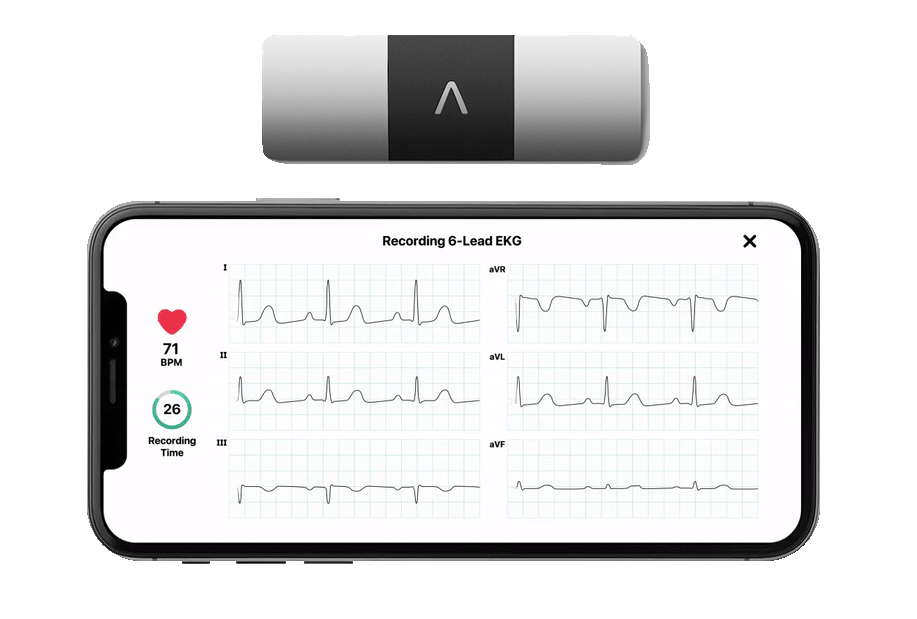


Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps it throughout your body. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is typically represented as two numbers, such as 120/80 mmHg. The top number, known as systolic pressure, indicates the pressure when your heart contracts, while the bottom number, called diastolic pressure, represents the pressure when your heart relaxes between beats.
Resting heart rate is the number of times your heart beats per minute while you are at rest. For adults, this rate typically ranges between 60 and 100 beats per minute. Heart sinus rhythm refers to the normal and regular rhythm of your heartbeat, which originates from the sinus node, the heart's natural pacemaker.
Lung function refers to how well your lungs exchange gases, specifically oxygen and carbon dioxide, between the air and your bloodstream. This process, known as respiration, is crucial for supplying your body with the oxygen it needs to operate and for removing carbon dioxide, which is a waste product.

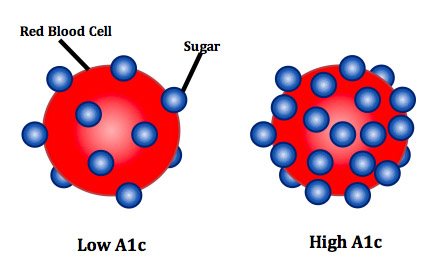


HbA1c, also known as glycated hemoglobin or glycosylated hemoglobin, is a blood test that indicates a person's average blood sugar levels over the past 2 to 3 months. It measures the percentage of red blood cells that have glucose attached to them, offering a long-term view of blood sugar control. This is different from a regular glucose test, which only reflects current blood sugar levels.
Triglycerides are a type of fat (lipid) present in your blood. They are the most common form of fat in your body and serve as a source of energy or are stored in fat cells. Triglycerides are derived from the food you eat, especially fatty foods, and are also made from excess calories that your body converts and stores. While some triglycerides are necessary for good health, elevated levels can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Uric acid is a waste product in the blood that forms when the body breaks down purines. Purines are naturally occurring substances found in the body and also present in certain foods and beverages. The kidneys filter uric acid from the blood, which is then excreted in urine. Elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, known as hyperuricemia, can lead to health issues such as gout and kidney stones. Further, higher uric levels can be associated with poor metabolic health.
Uric acid can be associated with; excessive indutrialised food, namely, sugar, alcohol, and dehydration.
Uric acid can be associated with; excessive indutrialised food, namely, sugar, alcohol, and dehydration.

-
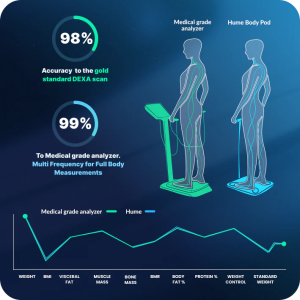
The Hume multi-frequency monitors measure bioelectrical impedance at six different frequencies. The lower frequencies assess the impedance outside the cell membrane, while the higher frequencies can penetrate the cell membrane. By measuring impedance at both lower and higher frequencies, it can calculate extracellular water & intracellular water, bone mass, muscle mass, and body fat. The algorithms will handle the rest.
#
Assessment
Why
1
Body fat composition
Fat mass (in kilograms) is a measurement that is relevant to you personally. For most people, the amount of subcutaneous fat (fat located just under the skin) is a more useful metric than body fat percentage. Additionally, it is important to consider body fat distribution, particularly the fat that accumulates around the heart.
2
Skeletal Muscle Mass
The total mass of muscles in kilograms that connect to your bones is a vital indicator of strength, mobility, and metabolic health. This measure is particularly important as we age, especially for women. I emphasise the significance of resistance exercise and its impact on maintaining skeletal muscle mass.
3
Skeletal Mass (bones)
The total mass of your skeletal system, which includes bones, cartilage, bone marrow, and other connective tissues, offers important information about the structural framework that supports your body and protects vital organs. This assessment can be especially valuable for individuals with lower body weight who are interested in starting resistance exercise.
4
Body water composition
Body water composition can offer insight into your hydration status. The critical numbers are water outside the cells and, more importantly, water inside the cells. Ideally, 66% of total water is located within the cells.
5
Grip Strength
Strong grip strength has been shown to predict negative health outcomes, such as cardiovascular disease, more accurately than systolic blood pressure. Activities like picking things up, cleaning, opening containers, engaging in favourite sports, and protecting against falls highlight the importance of grip strength.
